7 Advantages of Distributed Manufacturing
Distributed manufacturing promises to decentralize production capabilities, but that's not its only benefit. Read this article to discover seven advantages of distributed manufacturing.
In recent years, the world has witnessed a remarkable transformation in the realm of manufacturing. Traditional manufacturing processes have given way to a more innovative and sustainable approach known as distributed manufacturing powered by additive technology. This cutting-edge method allows for creating intricate and customized parts that can be produced in low volumes and closer to their end-use.
In this article, we will explore the numerous advantages of distributed manufacturing and why it represents the future of manufacturing.
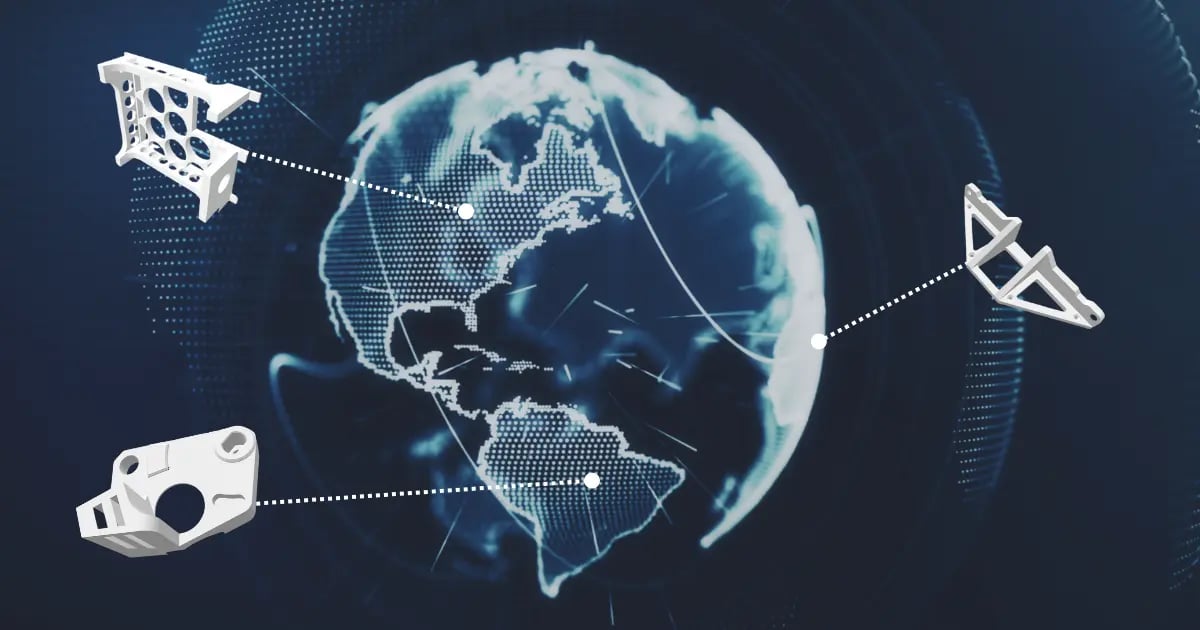
1. Decentralized Production
One of the main advantages of distributed manufacturing is its decentralized nature. Instead of relying on a few large centralized factories, additive technology allows production to be dispersed across numerous smaller facilities or even individual 3D printers. This decentralization reduces the need for long and resource-intensive supply chains, leading to significant cost savings and increased accessibility to manufacturing resources. By improving access to manufacturing, businesses can get the parts they need in less time, which can be a compelling business case in industries like energy and defense.
2. Customization and Personalization
Additive technology, or 3D printing, enables the creation of highly customized products. Unlike traditional mass production, which churns out identical items, distributed manufacturing allows for unique designs and tailored solutions. This customization is critical for optimizing existing part designs utilizing new manufacturing methods. With 3D printing, complex lattice structures can improve strength and performance while reducing weight, which is critical for aerospace or maritime applications.
 Pictured: Design engineer creating a custom 3D part using CAD software
Pictured: Design engineer creating a custom 3D part using CAD software
3. Reduced Material Waste
Traditional subtractive manufacturing methods often generate considerable material waste as excess material is carved away from the raw material. In contrast, additive technology builds products layer by layer, utilizing only the necessary amount of material. This reduction in waste not only helps conserve resources but also leads to substantial cost savings for manufacturers.
4. Sustainable and Eco-friendly
The global call for sustainability has never been louder, and distributed manufacturing aligns perfectly with this ethos. By eliminating the need for long transportation routes and minimizing material waste, additive technology significantly reduces the carbon footprint associated with manufacturing. Furthermore, 3D printing allows for the use of eco-friendly and recyclable materials, further enhancing the environmental benefits of distributed manufacturing.
5. Rapid Prototyping and Innovation
In traditional manufacturing, the development of prototypes can be time-consuming and costly. However, additive technology revolutionizes the prototyping process by enabling rapid iterations and modifications. Manufacturers can quickly create and test prototypes, allowing for more efficient product development and accelerated innovation. This improves go-to-market timelines by qualifying proven and tested designs before they're developed for high-volume production and injection molding.
6. Accessibility and Local Empowerment
Distributed manufacturing can be a game-changer for reducing reliance on cheap, globalized supply chains. By bringing the means of production closer to the end-users, this technology can empower local industry and reduce the dependency on imported goods. This increased accessibility can promote economic growth and foster innovation in previously lacking manufacturing capabilities.
7. Resilience and Disaster Response
The decentralized nature of distributed manufacturing makes it inherently resilient. In the face of supply chain disruptions or natural disasters, local production facilities equipped with 3D printers can quickly respond to the demand for critical goods and spare parts. This ability to produce essential items on demand enhances disaster preparedness and response capabilities.
Learn how 3YOURMIND accelerated production capabilities in response to COVID-19 and during the early weeks of Russia's full-scale military invasion of Ukraine.
Software for Distributed Manufacturing
Distributed manufacturing using additive technology represents a transformative leap forward in the world of manufacturing. Its decentralization, customization, reduced waste, and sustainability make it an attractive solution for businesses and consumers alike. Moreover, 3D printing's accessibility and local empowerment potential create opportunities for economic growth and innovation in various regions.3YOURMIND is a software platform that supports distributed manufacturing efforts. From part identification to order management and production, 3YOURMIND enables companies to find the best use cases for additive manufacturing, build digital inventories of 3D printable parts, and manage and schedule part production in one tool.
Request a demo to learn more.
Hear What Experts Are Saying About Distributed Manufacturing
Want to learn how to take distributed manufacturing from ideation to implementation? Watch this episode of 3D Talk Show to hear experts from Xometry, BCG, and Jabil discuss challenges and functional requirements to successfully realize a distributed manufacturing model.

